
Fx Co-Relations
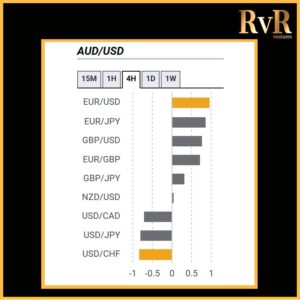
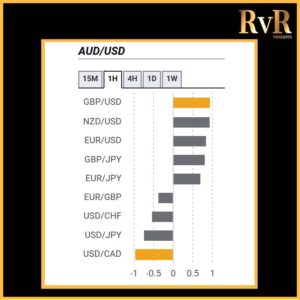
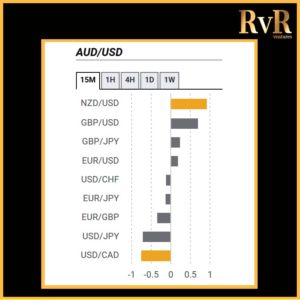
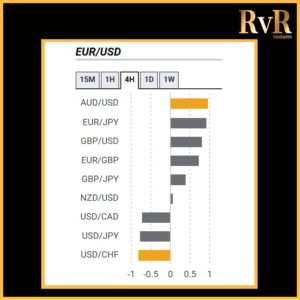
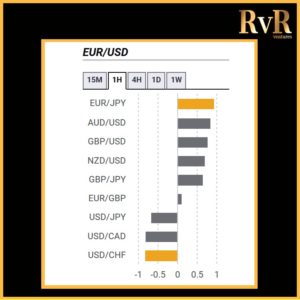
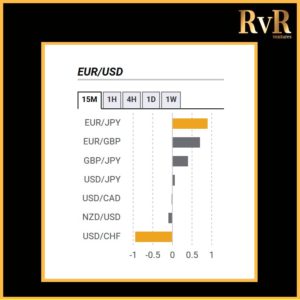
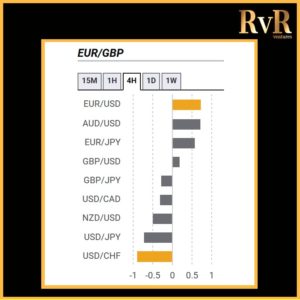
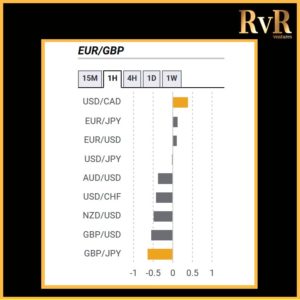
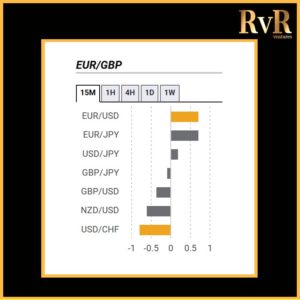
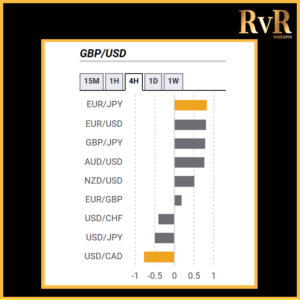
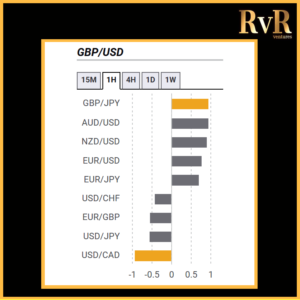
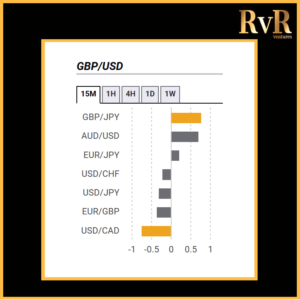
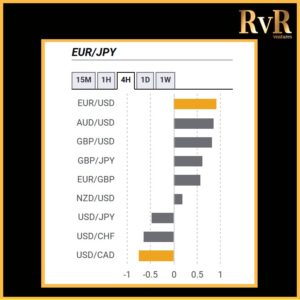
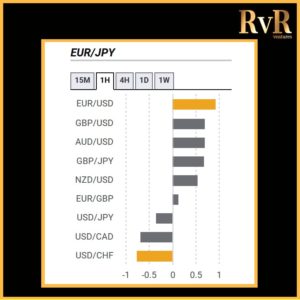
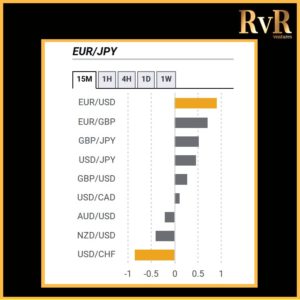
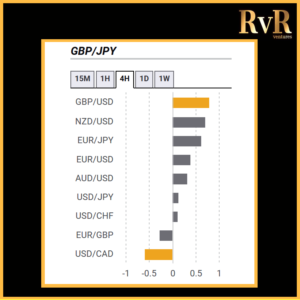
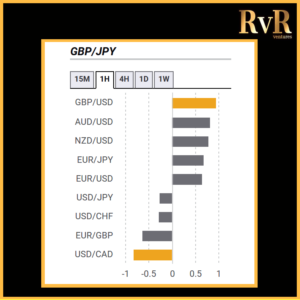
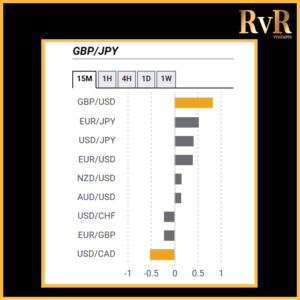
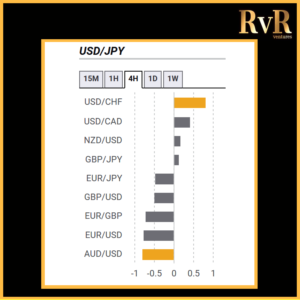
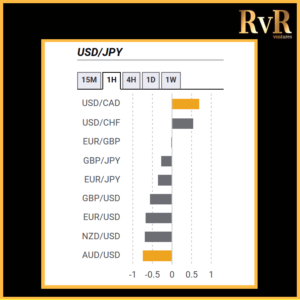
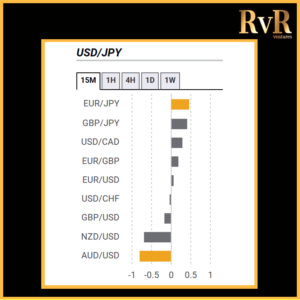
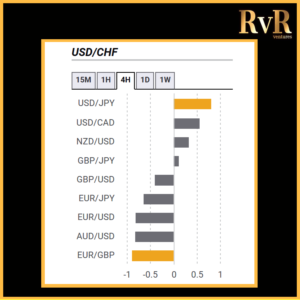
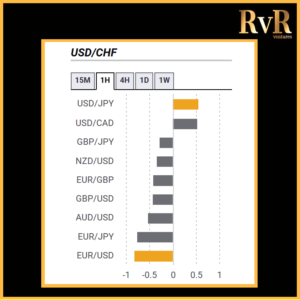
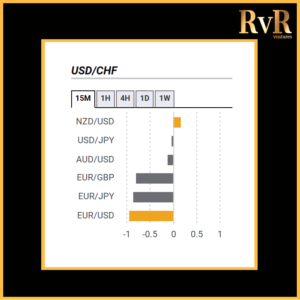
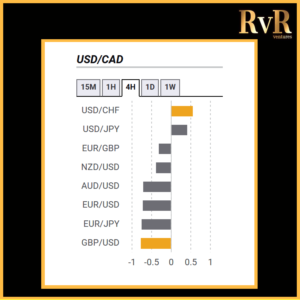
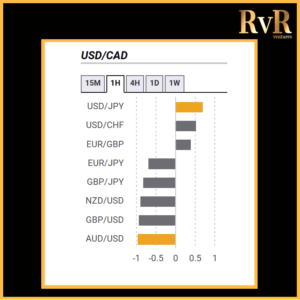
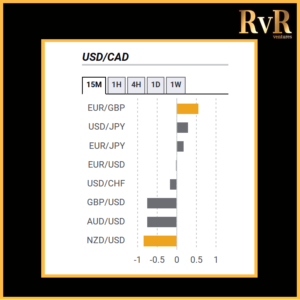
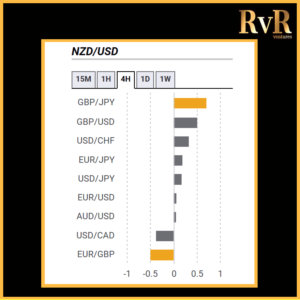
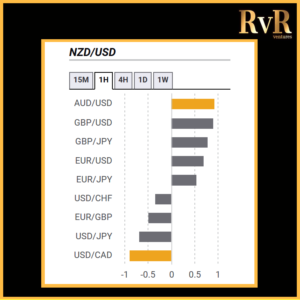
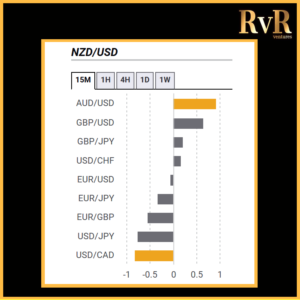
Understanding price relationships between various currency pairs allows you to get a more in-depth look at how to develop high-probability Forex trading strategies. Awareness of currency correlation can help to reduce risk, improve hedging, and diversify trading instruments. In this article, we will introduce you to Forex trading using intermarket correlations.
Meaning of currency pairs correlation in Forex
Correlation is a statistical measure of the relationship between two trading assets. Currency correlation shows the extent to which two currency pairs have moved in the same, opposite, or completely random directions within a particular period.
Analysis of two asset relationships using past statistical data has predictive value. By utilising the correlation coefficient, we can understand the relationship between two values and help manage risk. The coefficient is measured in decimal form from -1 to +1.
- A correlation of +1 shows that two currency pairs will move in the same direction 100% of the time. That is a perfect positive correlation. The correlation between EUR/USD and GBP/USD is a good example—if EUR/USD is trading up, then GBP/USD will also move in the same direction.
- A correlation of -1 indicates that two currency pairs will move in the opposite direction 100% of the time. EUR/USD and USD/CHF have a perfect negative correlation, thus if EUR/USD moves upwards, then USD/CHF goes downwards.
- A correlation of zero takes place if the relationship between currency pairs is completely random, which means they have no link at all.
Naturally, the stronger a positive or negative correlation, the higher a predictive value is drawn from the analysis. More extended time frames used for a technical analysis display more precise information compared to relationships over one minute, which have a little value. Monthly and yearly data generally provide the most reliable insight.
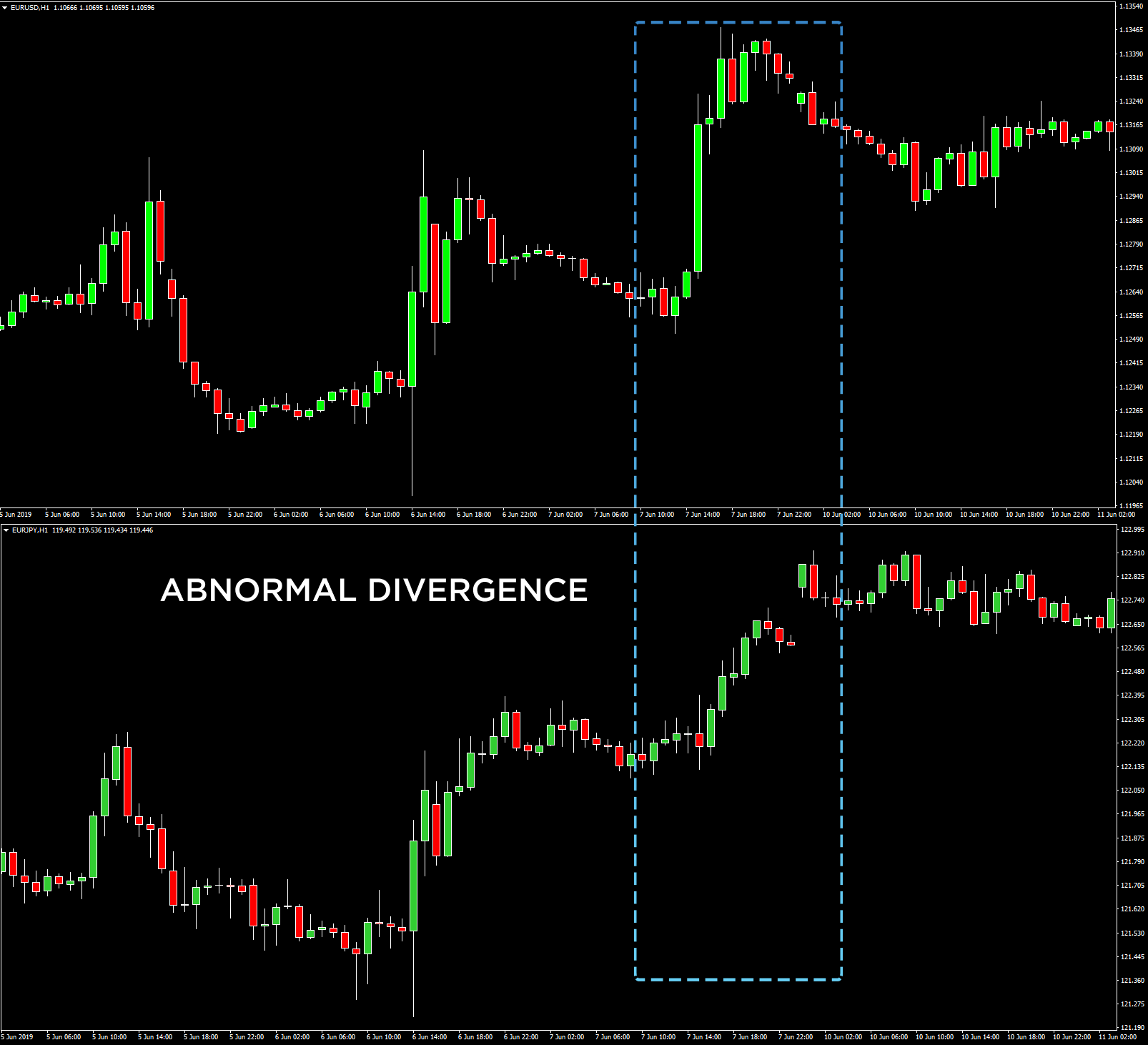
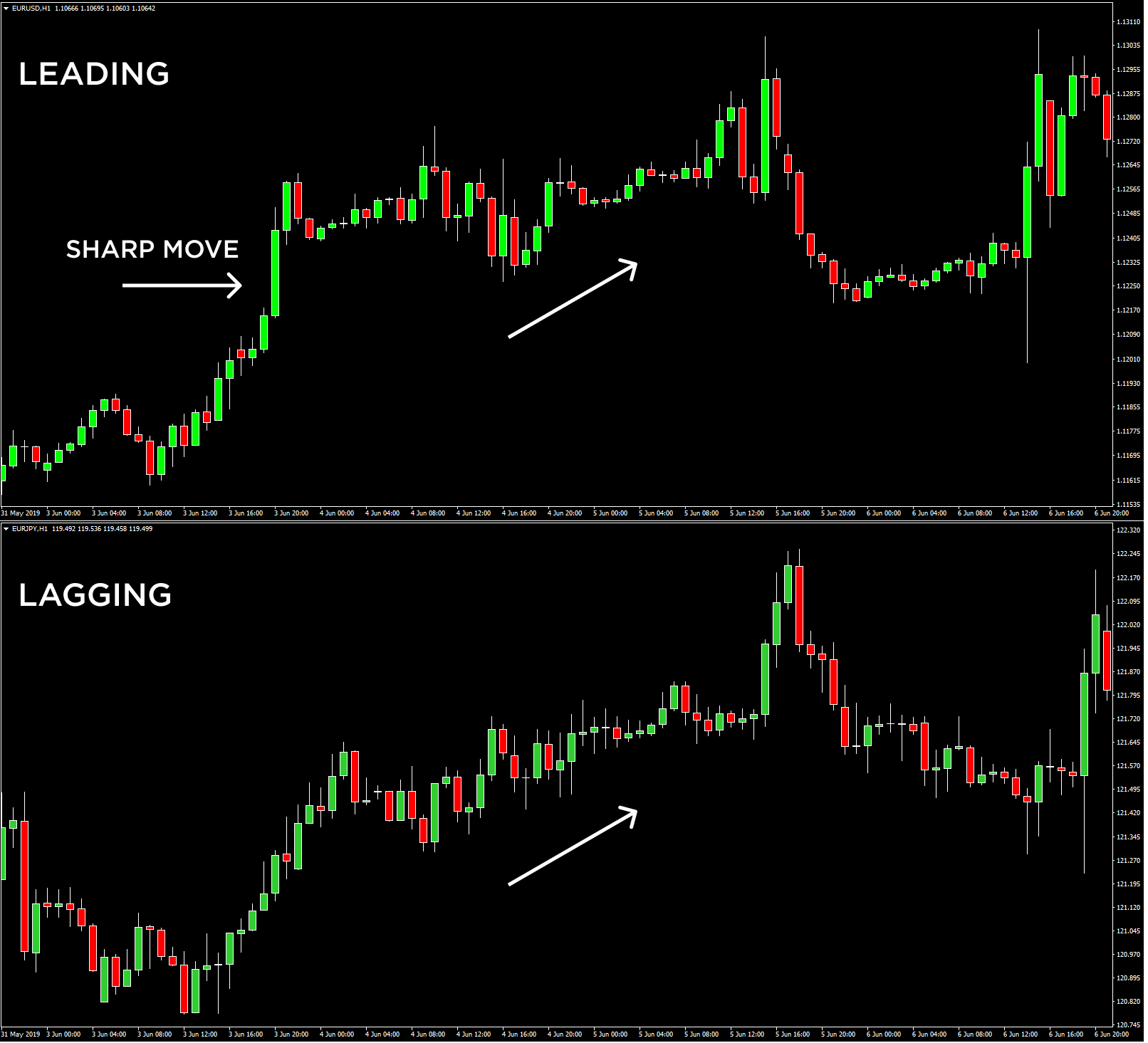 Impact of currency correlations on Forex trading
Impact of currency correlations on Forex trading
- They can form a basis of a statistically high probability Forex trading strategy.
- They can illustrate the amount of risk you are exposed to within your Forex trading account. For example, if you have bought several currency pairs with a strong positive correlation, then you are exposed to higher directional risk.
- You can avoid positions that effectively cancel each other out. EUR/USD and USD/CHF have a powerful negative correlation. If you have a directional bias, buying both EUR/USD and USD/CHF will counteract the moves in each pair.
- Understanding correlations can allow you to hedge or diversify your exposure to the Forex market.
- If you have a directional bias for a given currency, you can spread your risk using two strongly positive correlated pairs, in terms of diversification.
- If you are looking to hedge a position (holding it with low risk of losses) you can take a position in a negatively correlated pair. If you were to initiate a ‘long buy’ for EUR/USD, and it begins to move in an unfavourable direction, you can then hedge your position by purchasing a currency pair that has a negative correlation to EUR/USD, like USD/CHF.
Forex Trading strategies based on correlation
- When two pairs are highly correlated, one can serve as a leading indicator of the price movement of the other. If you see a sharp move in one of the two positively correlated pairs, you can anticipate a probable move in the other.
-
Correlation can be even a more powerful Forex tool for analysis in conjunction with other Forex indicators. For instance, if one pair breaks out above or below a significant technical level of support or resistance, the closely positively correlated pair has a high probability of the following risk.
-
If you notice two negatively correlated currency pairs and a significant upward price reversal in one pair takes place, then you can anticipate a potential downward reversal in the other pair. This is a price reversal.
-
Wait for an abnormal divergence between two highly correlated currency pairs and buy one and sell the other, with the expectation that they will converge in price movement again. This is a non-directional arbitrage exploiting currency correlations.
Highly correlated currency pairs in Forex
Examples of strong positive correlations (Yearly time frame): EUR/USD and GBP/USD (+ 0.89)
EUR/USD and AUD/USD (+ 0.81)
EUR/USD and EUR/CHF (+ 0.93)
AUD/USD and Gold (+ 0.75)
Examples of strong negative correlations (Yearly time frame): EUR/USD and USD/CHF (- 0.85)
USD/CAD and AUD/USD (- 0.88)
AUD/NZD and NZD/SGD (- 0.78)
USD/JPY and Gold (- 0.78)
Commodities that are correlated with currencies
-
The Canadian dollar and crude oil have a positive correlation because Canada is a significant oil producer and exporter.
-
Similarly, the Australian dollar and gold have a positive correlation because Australia is a significant gold producer and exporter. Both gold and the Japanese Yen are viewed as safe havens in times of uncertainty, and these two are also positively correlated.
-
Meanwhile, gold and the U.S. dollar typically have a negative correlation.
-
When the U.S. dollar starts to lose its value amid rising inflation, investors seek alternative stores of value such as gold.
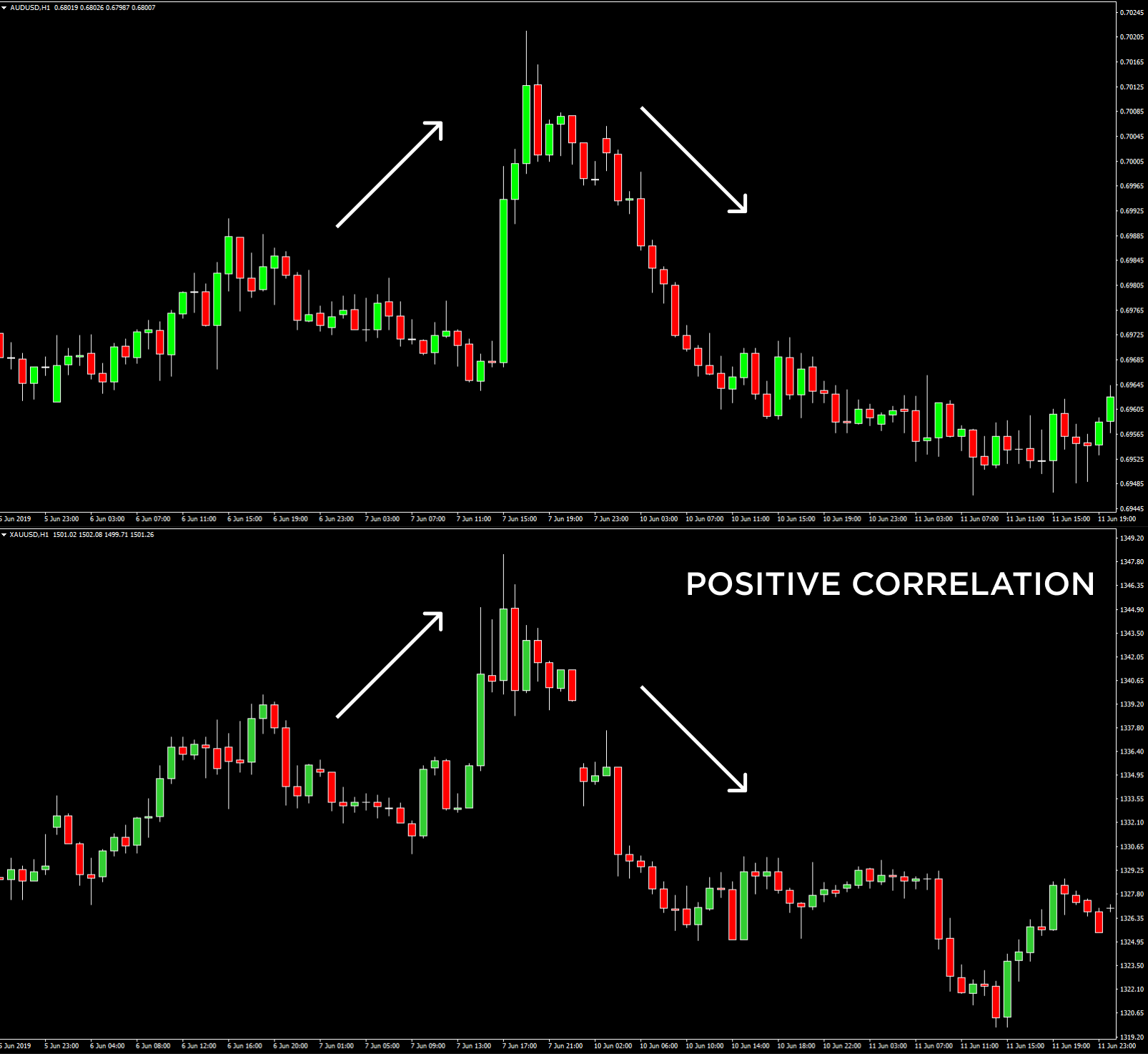
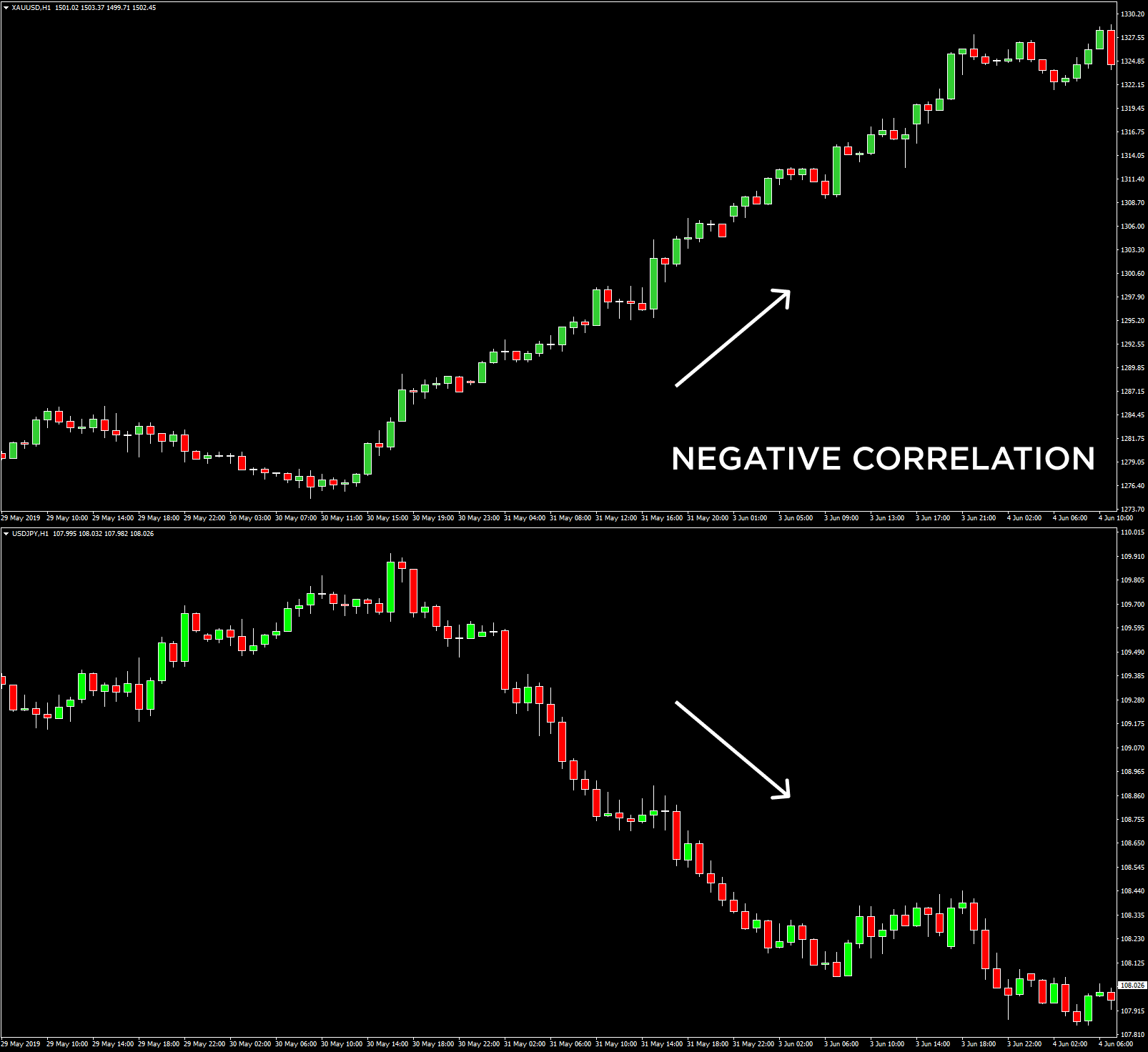
Currency correlations change in Forex
Be aware that currency correlations are continually changing over time due to various economic and political factors. These often include diverging monetary policies, commodity prices, changes in central banks’ policies, and more. Given that strong correlations can change over time, it highlights the importance of staying up to date in shifting currency relationships. We recommend checking long-term correlations to acquire a more in-depth perspective.
All in all, currency correlations could be a powerful tool you can use to develop high-probability trading strategies. You’ll also be aided in risk management, mainly if you track the correlation coefficients over daily, weekly, monthly and yearly time frames.
